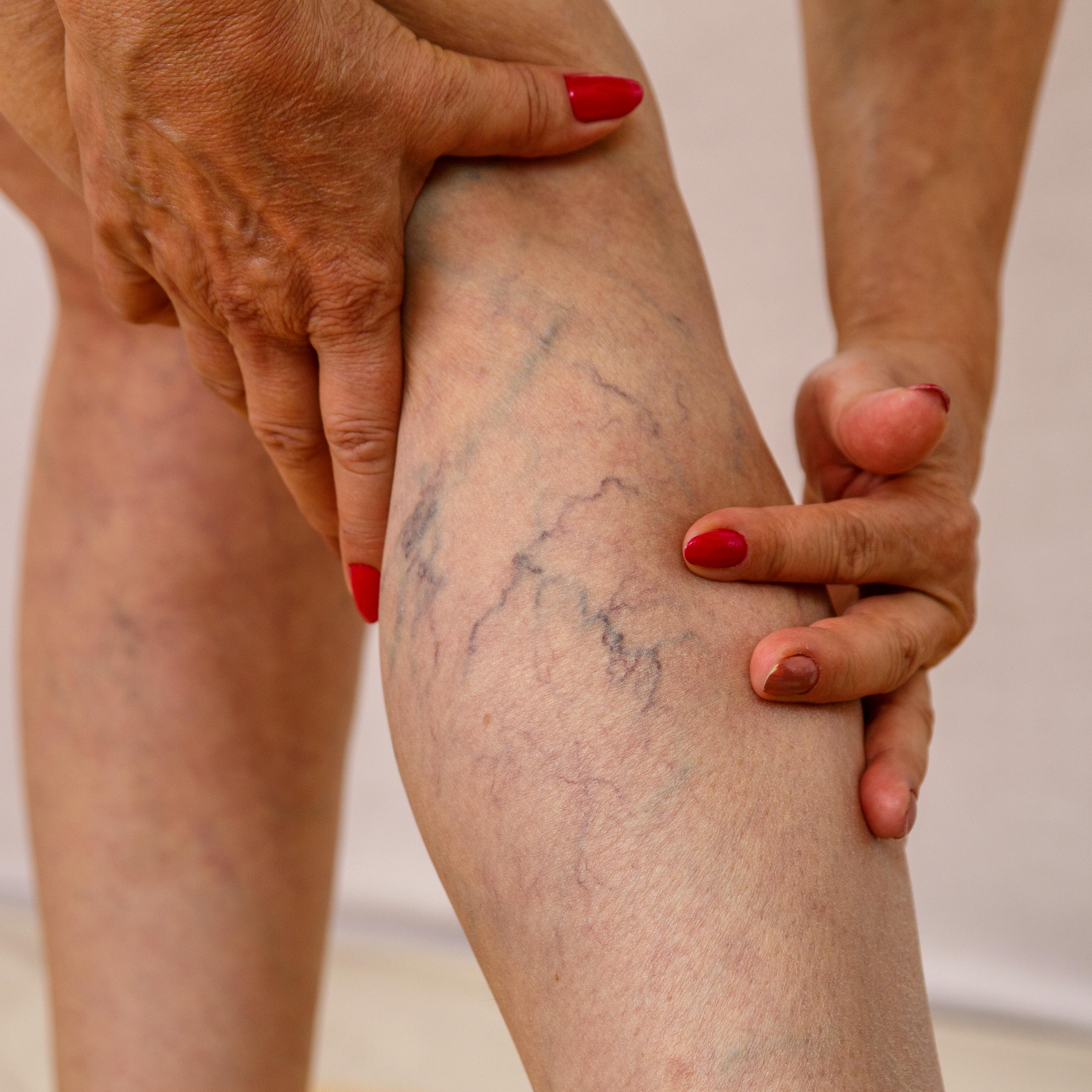
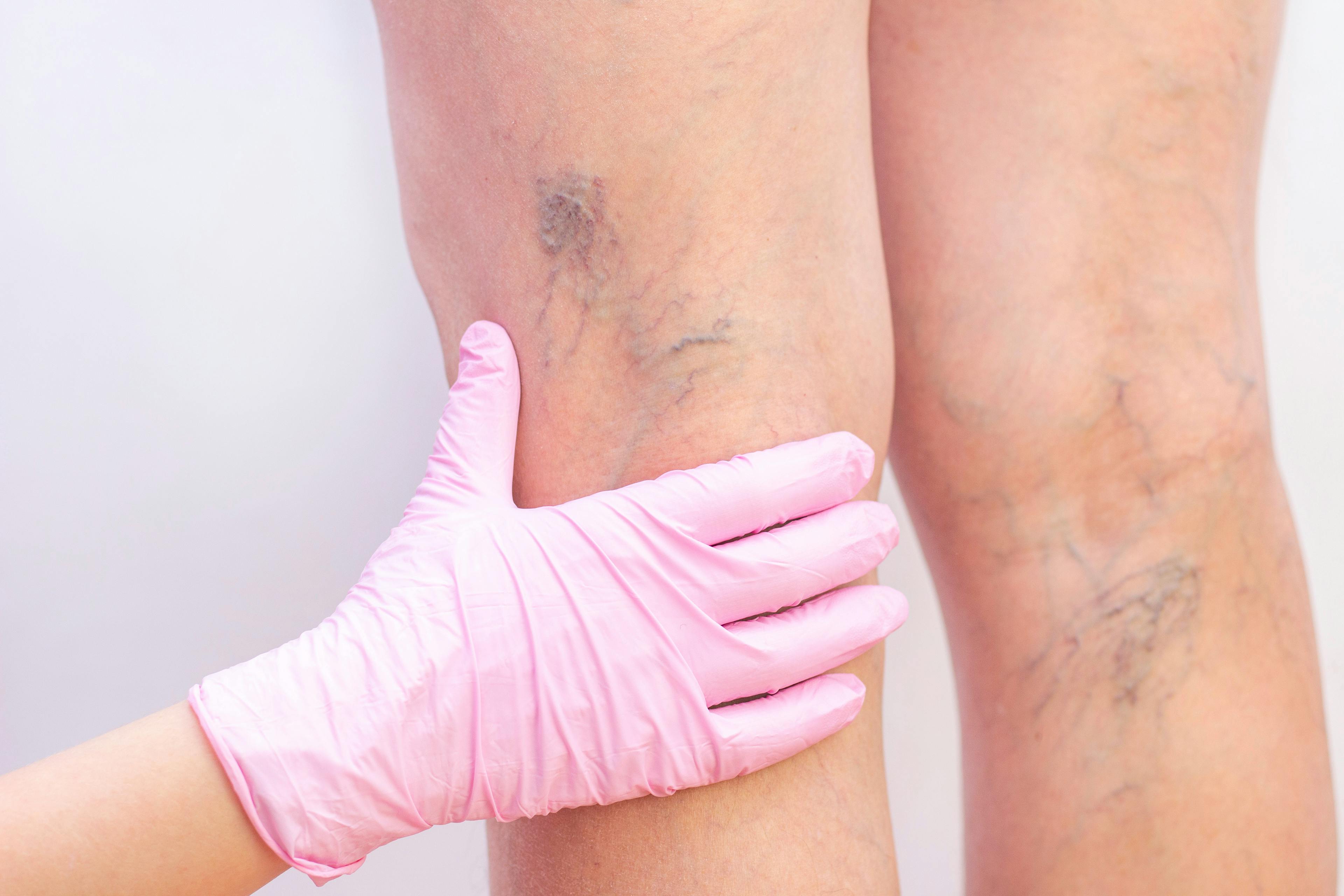
Healthy veins move blood from the legs back to the heart using one-way valves. When these valves weaken, blood begins to pool—causing varicose veins and, in more advanced stages, chronic venous insufficiency (CVI). These conditions affect nearly one in four U.S. adults and may lead to leg pain, swelling, and visible veins that worsen over time.
Early evaluation by a varicose vein specialist can help relieve discomfort, support healthy circulation, and prevent future complications.
What Are Varicose Veins and Chronic Venous Insufficiency?
Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted veins that often appear blue or purple beneath the skin, commonly affecting the legs and ankles. They develop when weakened valves allow blood to back up, causing the vein walls to stretch and distort.
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) is a more advanced form of venous disease, characterized by damaged valves that fail to return blood efficiently to the heart. This may cause persistent swelling, skin discoloration, or even venous ulcers in severe cases.
Note: Spider veins are smaller, surface-level veins that may occur with or without varicose veins but do not always indicate deeper valve dysfunction.
Common Symptoms and Warning Signs
Varicose veins and CVI often develop gradually and may worsen later in the day or after long periods of sitting or standing. Early symptoms include:
- Visible, bulging veins on the legs or ankles
- Heaviness, aching, or throbbing in the legs
- Itching, burning, or tenderness near the affected area
- Darkening or discoloration of the skin around the ankles
- Persistent leg swelling or fatigue
Seek immediate care if you develop redness, sudden swelling, warmth, or open sores—these may indicate a more serious condition, including a potential blood clot.
What Causes Varicose Veins and CVI?
Both conditions result from valve dysfunction that disrupts proper blood flow back to the heart, creating increased pressure within the veins.
Common causes include:
- Genetic predisposition or family history
- Aging, which weakens the vein walls and valves
- Prolonged sitting or standing
- Pregnancy, menopause, or hormonal changes
- Weight gain or obesity
While not all cases are preventable, lifestyle adjustments and early treatment can significantly reduce symptoms and progression.
Who Is at Risk?
Your risk increases if you are:
- Over age 50
- Female
- Pregnant or taking hormonal therapy
- Frequently standing or sitting for long periods
- Overweight
- From a family with a history of venous disease
Recognizing risk factors early can help you seek timely evaluation from a vein specialist.
How Are Varicose Veins Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically includes:
- An annual physical exam
- Duplex ultrasound to assess blood flow and detect valve reflux
- Doppler imaging or ankle-brachial index (ABI) testing to rule out arterial disease before treatment
These tests help determine whether you have cosmetic varicose veins or chronic venous insufficiency that requires targeted therapy.
Varicose Vein Treatment Options
CLS Health vein and vascular specialists in Webster and Pasadena offer personalized treatment plans that range from conservative care to minimally invasive procedures.
Conservative Treatments
- Compression stockings
- Leg elevation and regular walking
- Weight management
- Avoiding prolonged sitting or standing
Minimally Invasive Procedures
- Sclerotherapy: Injection therapy to close smaller or cosmetic veins.
- Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA) / Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): Heat therapy to seal damaged veins and redirect blood flow.
- Microphlebectomy: Removes larger surface veins through tiny incisions, often paired with ablation for optimal results.
Surgical Treatments (for Advanced CVI)
- Vein stripping
- Vein ligation
Modern surgical approaches use precise, image-guided techniques to maximize comfort and recovery.
When to Worry About Varicose Veins
Seek medical attention right away if you experience:
- Sudden swelling in one leg
- Warmth or redness (possible blood clot)
- Severe, persistent leg pain
- Open sores or ulcers near the ankle
- Rapid changes in skin color
Early treatment prevents complications such as venous ulcers or deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Which Specialist Should You See?
Varicose veins and CVI are best evaluated by a:
- Vascular surgeon, or
- Phlebologist (vein disease specialist)
Vascular surgeons provide the most comprehensive evaluation and treatment options for both cosmetic and medically necessary vein conditions.
Before your visit, track your symptoms and bring a list of medications. A referral from your primary care provider may be required, depending on your insurance plan.
Get Expert Varicose Vein Treatment in the Houston Area
Find lasting relief from leg pain, swelling, and visible veins with our board-certified vascular surgeons in Webster and Pasadena. We offer advanced diagnostic tools and minimally invasive treatments to restore circulation and comfort.
Schedule your consultation today and take the first step toward healthier, pain-free legs.
FAQs
No. While compression and exercise may ease symptoms, definitive treatment is usually required for long-term relief.
Not always. They can signal underlying venous disease that may worsen over time.
Yes. Activities like walking or swimming support healthy circulation.
Most accepted insurance plans cover medically necessary procedures for pain, swelling, or venous insufficiency. Cosmetic-only treatments may not be covered.