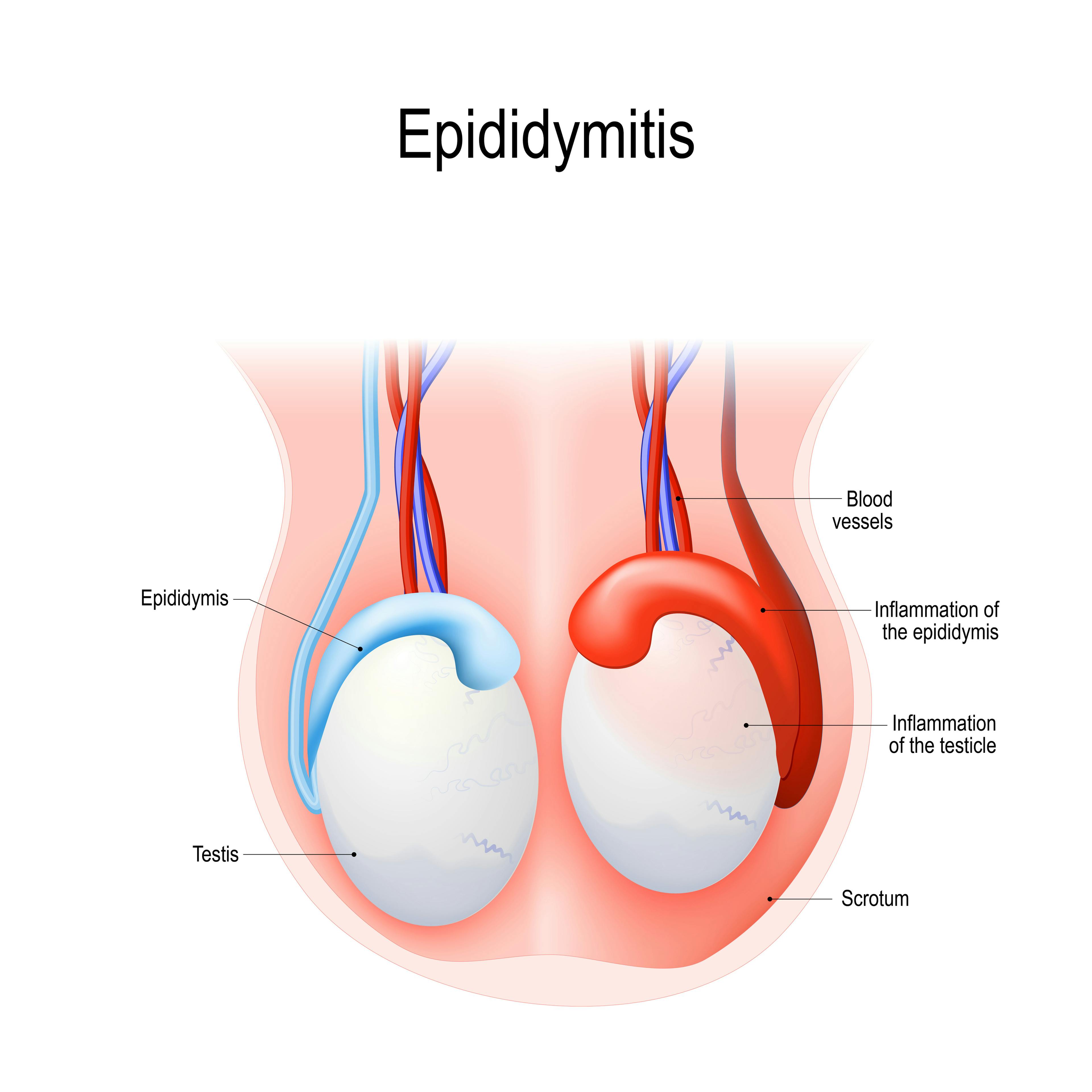
Epididymitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the epididymis, the tube responsible for storing and transporting sperm. With approximately 600,000 cases reported in the United States each year, epididymitis is relatively common.
What is Epididymitis?
When epididymitis occurs, the coiled tube at the back of the testicle that stores and transports sperm becomes inflamed. This inflammation often leads to pain, swelling, and tenderness in the scrotum and may also affect urinary and sexual health. It can result from factors such as:
- Bacterial infections (often from STIs like chlamydia or gonorrhea)
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs), especially in older men
- Physical trauma or irritation, from injury or prolonged catheter use, for example
This condition presents either acute epididymitis, which develops quickly, or chronic epididymitis, which persists over time.
Epididymitis Symptoms
Although the symptoms vary depending on the cause and severity, here are a few of the telltale signs of epididymitis:
- Pain or tenderness in one or both testicles
- Swelling or redness in the scrotum
- Painful urination or frequent urges to urinate
- Discomfort during ejaculation or the presence of discharge
- Fever, chills, or fatigue in more severe cases
If you're experiencing any of these symptoms, early intervention is key to rule out other conditions such as testicular torsion, orchitis, or urinary tract infections, and to prevent complications like abscess formation, chronic pain, or infertility.
Epididymitis Causes
Epididymitis may develop due to several factors, with infections being the primary cause. It may also result from physical trauma or other health conditions, such as:
- Bacterial Infections: STIs like chlamydia or gonorrhea are frequent culprits in younger men. Older men often experience epididymitis due to urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- Orchitis and Prostate Conditions: Inflammation in surrounding areas, such as the testicle (orchitis) or prostate, may extend to the epididymis.
- Physical Trauma or Irritation: Injuries, long-term catheter use, or even some medications can cause inflammation.
How to Know if You Have Epididymitis
A thorough evaluation, including a physical exam and several diagnostic tests, is needed to confirm epididymitis and identify its cause. Diagnostic procedure options include:
- STI Screening: When sexually transmitted infections are suspected, healthcare providers may perform urethral swabs or blood tests to detect bacteria like chlamydia or gonorrhea.
- Ultrasound for Epididymitis: An ultrasound allows doctors to examine the scrotum for swelling, fluid buildup, or other abnormalities. It also helps differentiate epididymitis from conditions like testicular torsion.
- Urine and Blood Tests: Urinalysis and blood tests provide valuable insights into infections or inflammation in the urinary and reproductive systems. These tests help confirm bacterial causes or rule out other possibilities.
Epididymitis Treatments
Treatment focuses on alleviating uncomfortable symptoms and addressing the root cause, whether bacterial or non-infectious.
Epididymitis Medication
For bacterial infections, antibiotics like doxycycline or Cipro (ciprofloxacin) are often the first line of treatment. These medications target the bacteria causing the inflammation, and it's important to complete the full course of antibiotics to fully clear the infection.
Epididymitis Surgery
In rare cases, surgery may be necessary, especially if abscesses need to be drained or if the inflammation is severe and persistent. Surgery may also be considered for chronic or recurrent cases that do not respond to other treatments. Under these circumstances, consulting a urology specialist can help determine the most appropriate course of action and ensure you receive the best possible care.
Ice Packs for Epididymitis
To reduce swelling and alleviate pain from epididymitis, apply a cold compress to the scrotum. Wrap ice packs or chilled gel packs in a soft cloth to create a barrier between the ice and your skin. Apply for 15-20 minutes every hour as needed during the initial 48 hours. This helps constrict blood vessels, decrease swelling, and numb the pain in the area.
Hydration and Rest
Proper hydration contributes to recovery from epididymitis. Drink 8-10 glasses of water daily to help flush out bacteria and support immune function, avoiding caffeine and alcohol. Rest is also critical; minimize physical activity that strains the scrotal area and use cushions to elevate your hips and reduce swelling. These practices promote faster healing by supporting your body's natural defenses and recovery processes.
How to Prevent Epididymitis
While not all cases of epididymitis are preventable, some steps help reduce your risk:
- Practice Safe Sex: Using condoms reduces the risk of STIs, which are a leading cause in younger men.
- Treat UTIs and Prostate Conditions Promptly: Early intervention for urinary tract infections or prostate issues prevents bacteria from spreading to the epididymis.
- Minimize Testicular Trauma: Wear protective gear during physical activities that might result in scrotal injury.
FAQs
The duration depends on the type and severity of the condition. Acute cases typically improve within a week or two with proper treatment, while chronic epididymitis may require longer management and ongoing monitoring.
Epididymal cysts form when fluid builds up in the epididymis, often due to blockages or previous inflammation. While usually painless and benign, they can become noticeable if they grow in size.
No, epididymitis itself is not contagious, but infections like chlamydia or gonorrhea that cause it are transmissible. Using protection and treating infections promptly safeguards both partners’ health.
In severe or untreated cases, epididymitis may result in scarring or blockages that impact sperm transport. Early diagnosis and treatment reduce this risk and help preserve fertility.
Yes, non-STD causes include urinary tract infections, physical trauma, or prolonged use of certain medical devices like catheters. These cases are more common in older men or those with preexisting urinary issues.