Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common issue that affects men of all ages, with nearly 30 million men in the United States experiencing some degree of ED. It is characterized by the inability to achieve or maintain an erection suitable for sexual intercourse. While the prevalence of ED increases with age, it is not an inevitable part of aging and can often be treated with the help of a professional.
What Is Erectile Dysfunction?
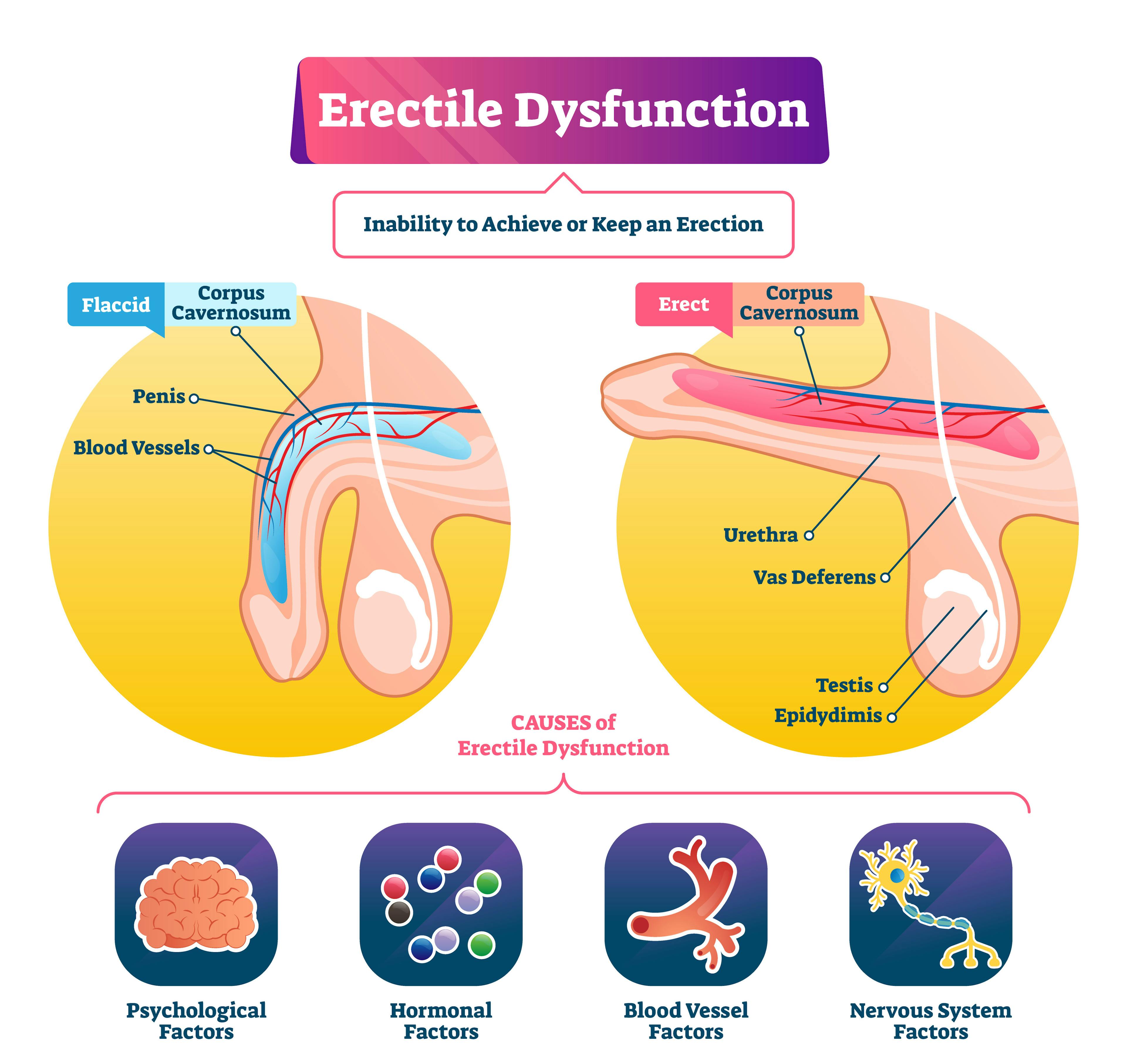
Erectile dysfunction is a condition where a man finds it difficult to achieve or sustain an erection firm enough for sexual intercourse. Often referred to as "impotence," ED can significantly impact quality of life and relationships, and sometimes indicates underlying health issues that require attention. Although erectile dysfunction is more frequently diagnosed in older men, men of all ages can experience ED.
Erectile Dysfunction Symptoms
Several key symptoms directly influence sexual function in cases of erectile dysfunction. The primary symptoms include:
- Trouble achieving an erection
- Difficulty keeping an erection during sexual activities
- Reduced libido
- Premature ejaculation
- Delayed ejaculation
These symptoms may occur intermittently or persistently, varying in frequency and severity.
Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
Male sexual arousal is a complex process, and ED can stem from both physical and psychological factors.
- Physical causes: ED may be caused by cardiovascular issues such as heart disease, metabolic conditions like diabetes, hormonal imbalances including low testosterone, or other disorders affecting blood flow or nerve function.
- Psychological causes: Stress, anxiety, depression, and relationship problems are common psychological triggers for erectile dysfunction.
Other contributing factors including alcohol and substance use, certain medications, and sleep disorders can also influence the occurrence of ED.
Diagnosis of Erectile Dysfunction
The diagnosis of ED involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examinations, and possibly diagnostic testing.
If you consistently have difficulty getting or keeping an erection, consider consulting a urologist. Your physician will likely perform tests, which may include blood tests to assess general health and hormone levels, urine tests to check for diabetes or other underlying health conditions, and an ultrasound to evaluate blood flow to the penis. In some cases, a psychological examination may also be proposed to identify any emotional or psychological causes.
Treatments for Erectile Dysfunction
ED Medications
Oral medications are a common first-line treatment for erectile dysfunction. These include Viagra, Cialis, and Levitra, which enhance the effects of nitric oxide—a natural chemical your body produces that relaxes muscles in the penis, increasing blood flow.
Testosterone Replacement Therapy
For men with low testosterone levels, testosterone replacement therapy is administered in several forms, including gels, patches, or injections. This treatment addresses symptoms associated with low testosterone, such as erectile dysfunction, low mood, and reduced energy levels, to support overall health.
Exercise
Regular physical activity helps to improve circulation, lower stress, and contribute to overall health, which may help reverse ED naturally.
Penile Implants
For men who do not respond to other treatments, penile implants offer a more permanent solution. This surgical option involves placing devices into both sides of the penis, which allows manual control of erections.
Need Treatment Now?
If ED is affecting your confidence and quality of life, you don’t have to face it alone. A urology specialist can help you identify the underlying cause and find the right solution for your individual situation, whether it's medication, hormone therapy, lifestyle adjustments, or advanced procedures.
FAQs
No, ED is not necessarily permanent. Many cases can be managed with medications, as well as lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and reducing alcohol consumption. Various therapies are also available, depending on the underlying cause of the ED.
ED can occur at any age, but it is more common in men older than 50. In fact, research shows that by age 50, around 50% of men report experiencing episodes of mild to moderate ED. Early signs may start as mild difficulty with erections which gradually become more challenging and frequent with time.
Yes, it is possible for high blood pressure to impair blood flow to the penis, potentially causing erectile dysfunction. It can also damage blood vessels over time, limiting their ability to supply sufficient blood for maintaining an erection. Moreover, some medications for high blood pressure might contribute to ED.
Absolutely. Stress affects the body in many ways and can lead to psychological ED by disrupting the signals between the brain and the penis that initiate an erection.
Aside from traditional treatments like medications and surgery, recent advancements include low-intensity shock wave therapy, which is thought to promote blood vessel growth and improved blood flow to the penis.
