Advanced Treatment Options for Stronger, Healthier Hearts
When testing or imaging reveals a heart or vascular condition, the next step is precise, personalized treatment. At CLS Health, our board-certified cardiologists, vascular surgeons, and electrophysiologists perform a full spectrum of minimally invasive, interventional, and surgical procedures to restore circulation, correct heart rhythm problems, and protect long-term heart function.
From same-day procedures to advanced heart surgeries, our team uses the latest technology and techniques to help you heal faster, feel better, and return to your normal activities safely.
Procedures for Arrhythmia and Heart Rhythm Monitoring
Irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias) can range from mild to life-threatening. Our electrophysiology specialists diagnose and treat rhythm disorders using advanced monitoring and minimally invasive therapies designed for accuracy and comfort.
Procedures include:
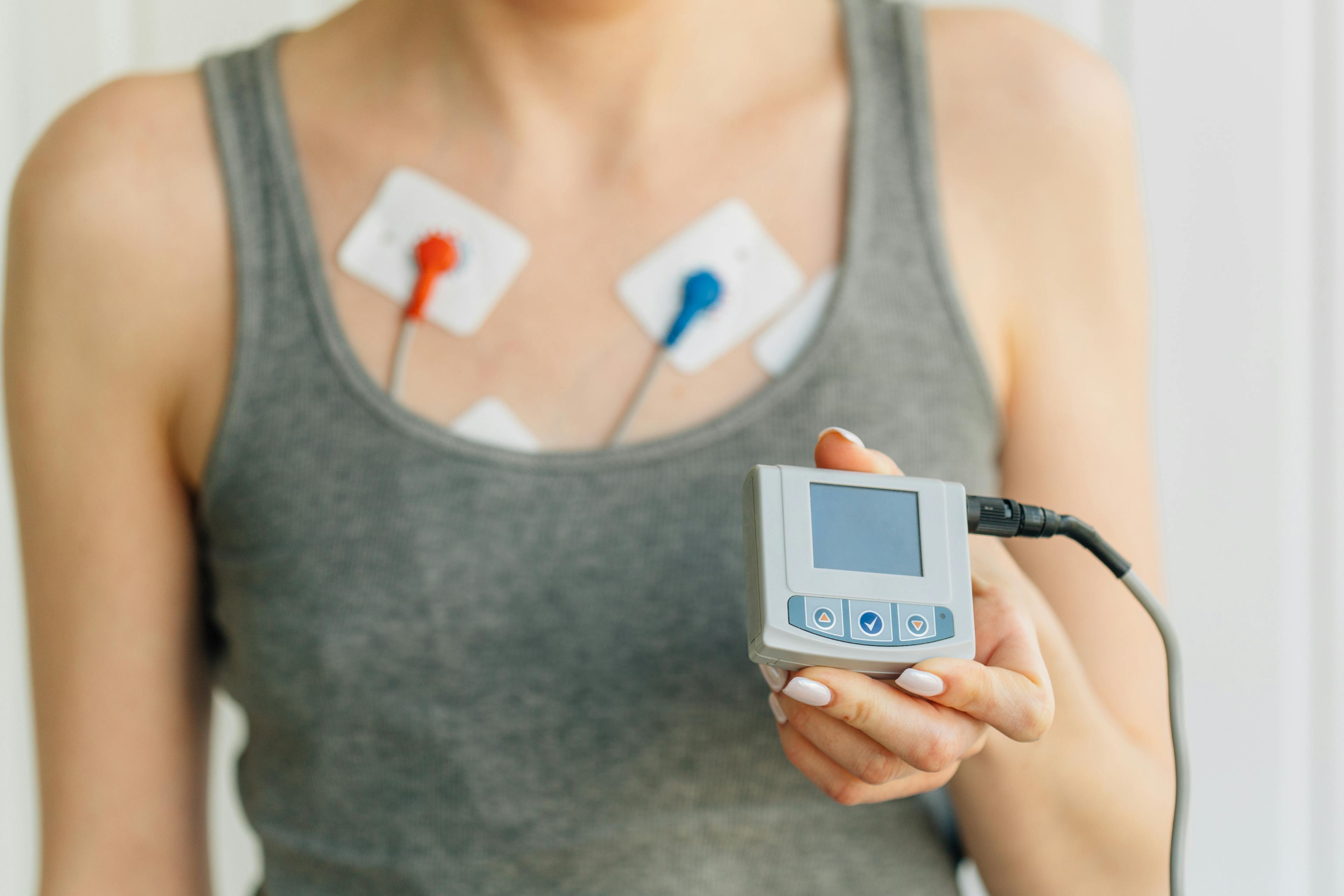
- Holter and Event Monitors – Portable devices that record your heart rhythm over hours or days to detect irregularities.
- Cardioversion – A controlled, gentle electrical pulse to restore normal rhythm.
- Catheter Ablation – A minimally invasive procedure that targets and eliminates heart tissue causing abnormal electrical signals.
- Pacemaker Implantation – A small device placed under the skin to regulate slow or irregular heartbeats.
- ICD (Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator) Placement – A life-saving device that detects and corrects dangerous heart rhythms automatically.
These treatments help control symptoms like palpitations, dizziness, and fatigue—allowing patients to live active, confident lives.
Interventional Cardiology Procedures
Our interventional cardiology team specializes in catheter-based procedures that treat blocked or narrowed arteries without traditional surgery. These procedures are typically performed through a small incision, resulting in quicker recovery and less discomfort.
Common procedures include:
- Cardiac Catheterization – A diagnostic and treatment procedure that assesses blood flow and identifies blockages.
- Angioplasty – A technique using a small balloon to open narrowed arteries and restore healthy circulation.
- Stenting – Placement of a tiny mesh tube (stent) to keep arteries open after angioplasty and prevent future blockages.
These procedures are key in treating coronary artery disease, preventing heart attacks, and improving long-term heart health.
Complex and Surgical Procedures
For patients with advanced heart or vascular disease, our specialists offer a full range of surgical and hybrid procedures—including minimally invasive and robotic-assisted approaches whenever possible.
Procedures include:
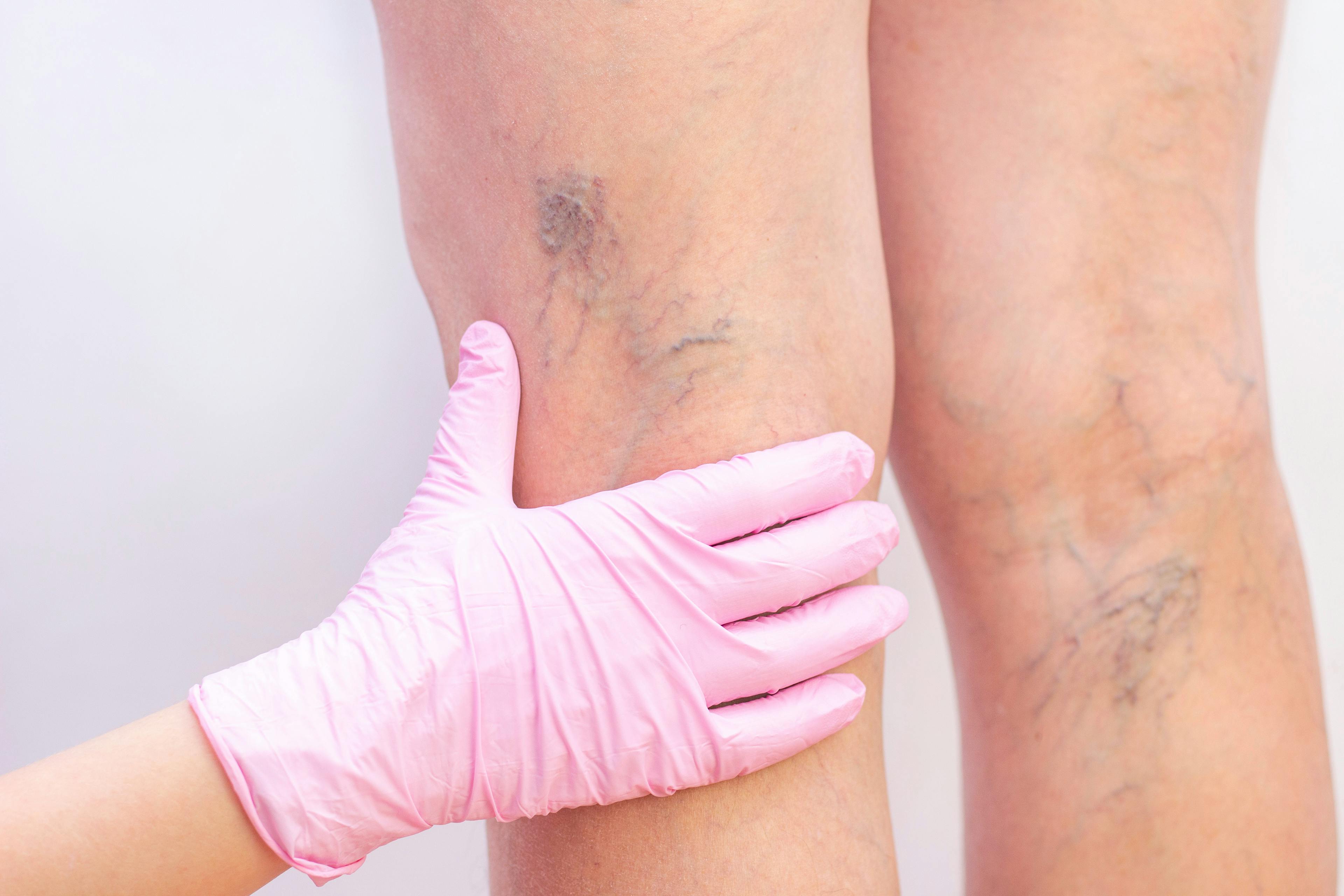
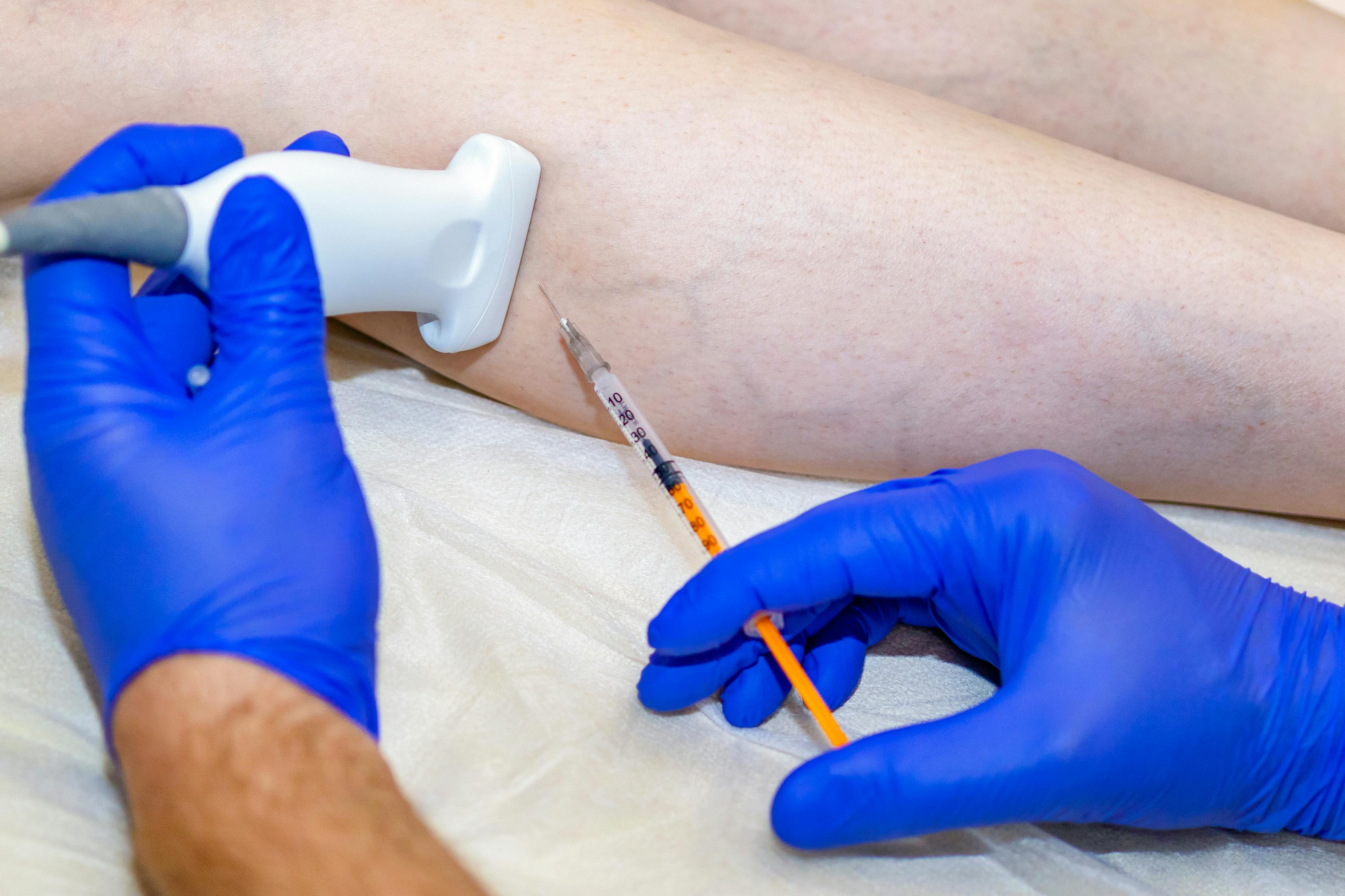
- Vein Ablation – A minimally invasive treatment for varicose veins and venous insufficiency.
- Mitral Valve Repair and Heart Valve Replacement – Restores proper blood flow through the heart valves.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) – Creates new routes around blocked arteries to improve blood flow to the heart.
- Robotic-Assisted and Minimally Invasive Cardiac Surgeries – Performed through smaller incisions for faster recovery and reduced hospital stays.
- Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR) – A nonsurgical alternative for replacing a diseased aortic valve through a catheter.
- Heart Transplant Procedures – Comprehensive transplant evaluation, surgery, and lifelong post-transplant care for end-stage heart failure patients.
Every treatment plan is guided by your condition, health goals, and lifestyle—combining medical precision with compassionate care.
Why Patients Trust CLS Health for Cardiac and Vascular Procedures
At CLS Health, our multidisciplinary heart and vascular team brings together experts in interventional cardiology, electrophysiology, cardiac surgery, and vascular medicine—all working together to deliver seamless, coordinated care.
- Advanced, minimally invasive options for faster recovery
- Access to state-of-the-art cardiac imaging and hybrid operating suites
- Personalized pre- and post-procedure care plans
- Continuous monitoring and long-term heart health management
We’re here not only to perform your procedure but to help you thrive—before, during, and after treatment.
Schedule Your Consultation
If you’ve been diagnosed with a heart or vascular condition—or if you’re ready to explore advanced treatment options—CLS Health is here to help. Our specialists will review your results, explain your options, and design a plan tailored to your needs and goals.
Take the next step toward a stronger heart and healthier life.
Schedule your consultation with a heart and vascular specialist today.