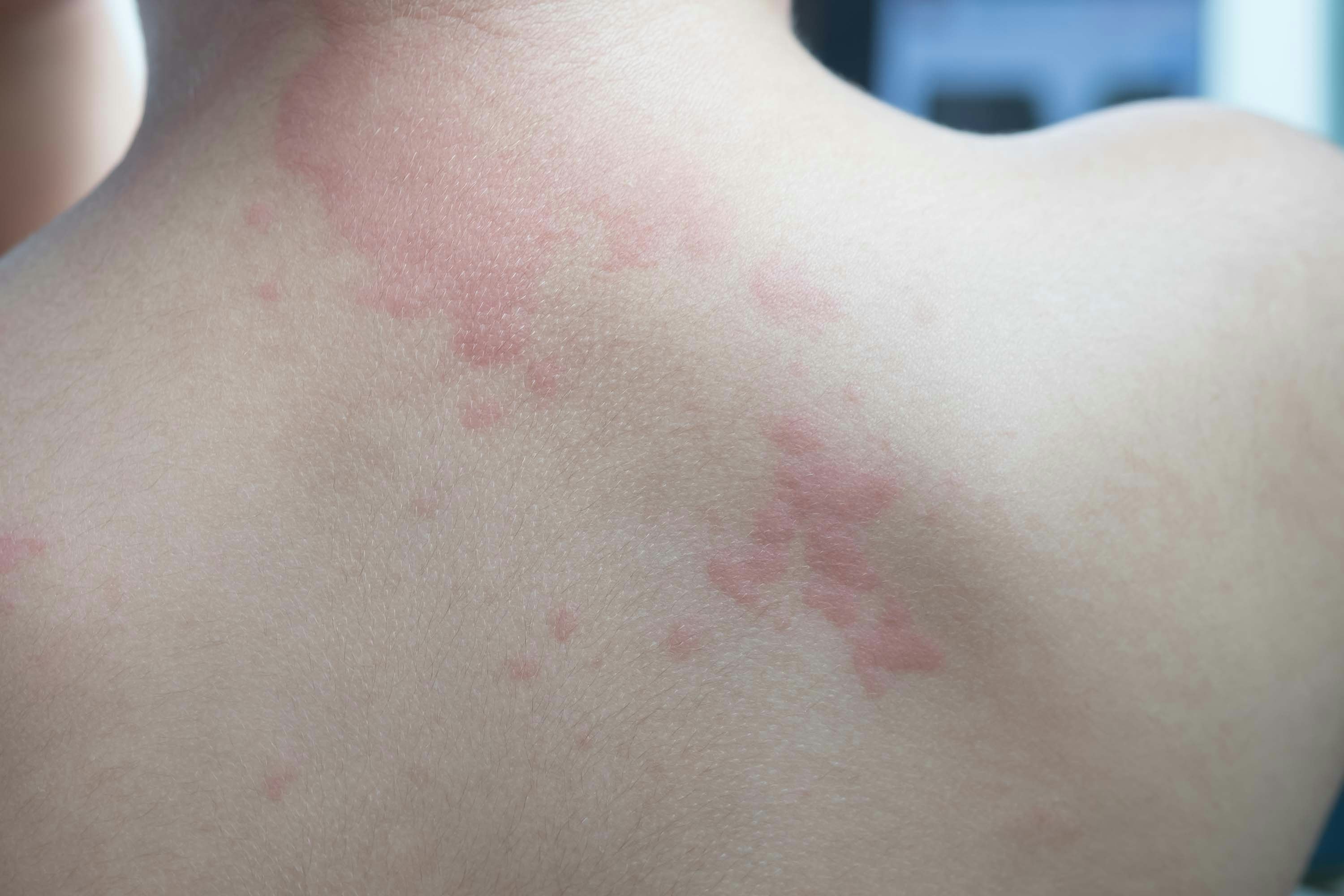
You wake up with red, itchy welts across your skin. They fade after a few hours, only to return to a new spot the next day. You start avoiding foods, changing detergents, and wondering if you’re allergic to something—but nothing helps.
If this sounds familiar, you may be dealing with spontaneous urticaria, also known as chronic hives, when symptoms last for six weeks or more. Unlike allergy-related hives, spontaneous urticaria has no clear trigger, making it one of the most misunderstood skin conditions.
The good news? It’s common, real, and very treatable.
What is Spontaneous Urticaria?
Spontaneous urticaria refers to hives that appear without a clear trigger.
- If hives occur almost daily for 6 weeks or longer, it’s called chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU).
- If they come and go but haven’t lasted that long yet, it’s simply spontaneous urticaria.
This term has replaced older labels like “idiopathic urticaria.”
Symptoms: What Do Hives Look Like?
- Raised, red, itchy welts that shift from one area of the body to another
- Last a few hours in one spot before fading, then reappear elsewhere
- May include angioedema (swelling of lips, eyelids, hands, or feet)
Why Hives Aren’t Always an Allergy
While short-term hives (hours to days) can be allergic, spontaneous urticaria isn’t usually caused by food or allergens. Instead, the immune system activates on its own, releasing histamine without a trigger.
That’s why:
- Allergy testing is usually negative
- Food elimination diets are not effective
- Symptoms can flare regardless of diet or environment
Possible aggravators: stress, illness, or temperature changes — but these aren’t root causes.
Myths vs. Facts About Chronic Hives
Myth 1: Hives always mean I’m allergic to something.
Fact: Most chronic hives are not allergy related.
Myth 2: Nothing can be done for chronic hives.
Fact: Today, there are effective treatment pathways from antihistamines to biologic therapies.
Treatment Options for Chronic Hives
Chronic hives are treatable, often with a stepwise approach:
- Antihistamines – May require higher-than-standard doses (under physician supervision, per international guidelines).
- Biologic therapy – For patients not controlled with antihistamines, omalizumab (Xolair) injections are safe and highly effective.
- Screening for underlying conditions – In select patients, testing for autoimmune issues (like thyroid disease) may be appropriate.
Most patients improve over time, but treatment can greatly improve comfort and quality of life while hives are active.
When to See a Specialist
Contact an Allergist/Immunologist if your hives:
- Do not improve with over-the-counter antihistamines
- Are accompanied by swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat
When to Seek Emergency Care
Call 911 or go to the ER if you ever develop:
- Trouble breathing or swallowing
- Swelling of the tongue or throat
- Dizziness, fainting, or a feeling of your throat closing
These may signal anaphylaxis, a life-threatening reaction, which is very different from chronic spontaneous urticaria.
Relief from Chronic Hives Is Here: Expert Treatment in Houston
Living with chronic hives can feel overwhelming—but you don’t have to suffer in silence. At CLS Health, our Allergy & Immunology team specializes in diagnosing and treating spontaneous urticaria. From advanced antihistamine regimens to biologic therapies like omalizumab (Xolair), we provide personalized treatment plans that bring real relief.
If you’re searching for hives treatment in Houston, our specialists are ready to help you take control of your symptoms and get back to living comfortably.