Protecting Your Vascular Health with Expert Diagnosis and Treatment
Vascular disease affects the network of arteries and veins that carry blood throughout the body. When blood vessels become narrowed, blocked, or weakened, it can lead to pain, swelling, or even life-threatening complications like stroke or limb loss. Early diagnosis and expert care are key to improving circulation, relieving symptoms, and protecting long-term vascular health.
Treatment plans may include lifestyle changes, medications, minimally invasive procedures, or surgery when needed to restore blood flow and prevent complications.
Conditions We Treat
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
PAD occurs when the arteries in the legs become narrowed or blocked by plaque buildup, reducing blood flow to the muscles. It can cause claudication, or pain and cramping in the legs during activity, and may progress to critical limb ischemia (CLI)—a severe blockage that can lead to wounds, ulcers, persistent pain, or risk of limb loss. Treatment may include exercise therapy, medications, angioplasty with stenting, or surgical bypass to restore blood flow.
Aortic Aneurysms
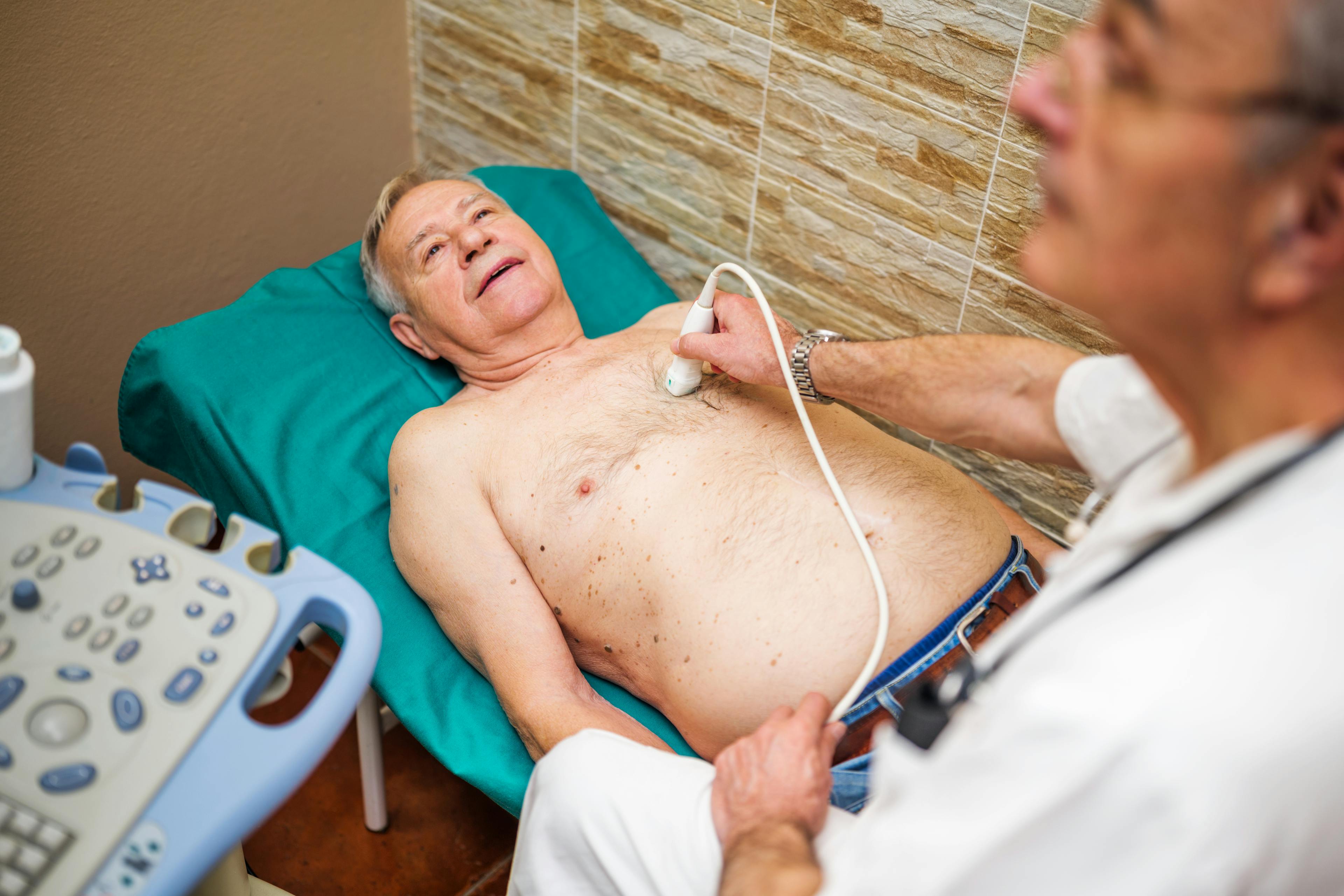
An aneurysm is an abnormal bulge or ballooning in the wall of an artery, most commonly the abdominal aorta. If left untreated, an aneurysm can rupture and cause life-threatening bleeding. Diagnosis often involves vascular ultrasound or CT imaging. Depending on size and risk, treatment may include ongoing monitoring, endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR), or open surgical repair.
Carotid Artery Stenosis
A narrowing of the carotid arteries, which supply blood to the brain. This significantly increases the risk of stroke, which can cause sudden symptoms such as weakness, numbness, speech difficulty, or vision changes. Treatment may involve medications to reduce stroke risk, carotid artery stenting, or carotid endarterectomy, a surgical procedure to remove plaque buildup.
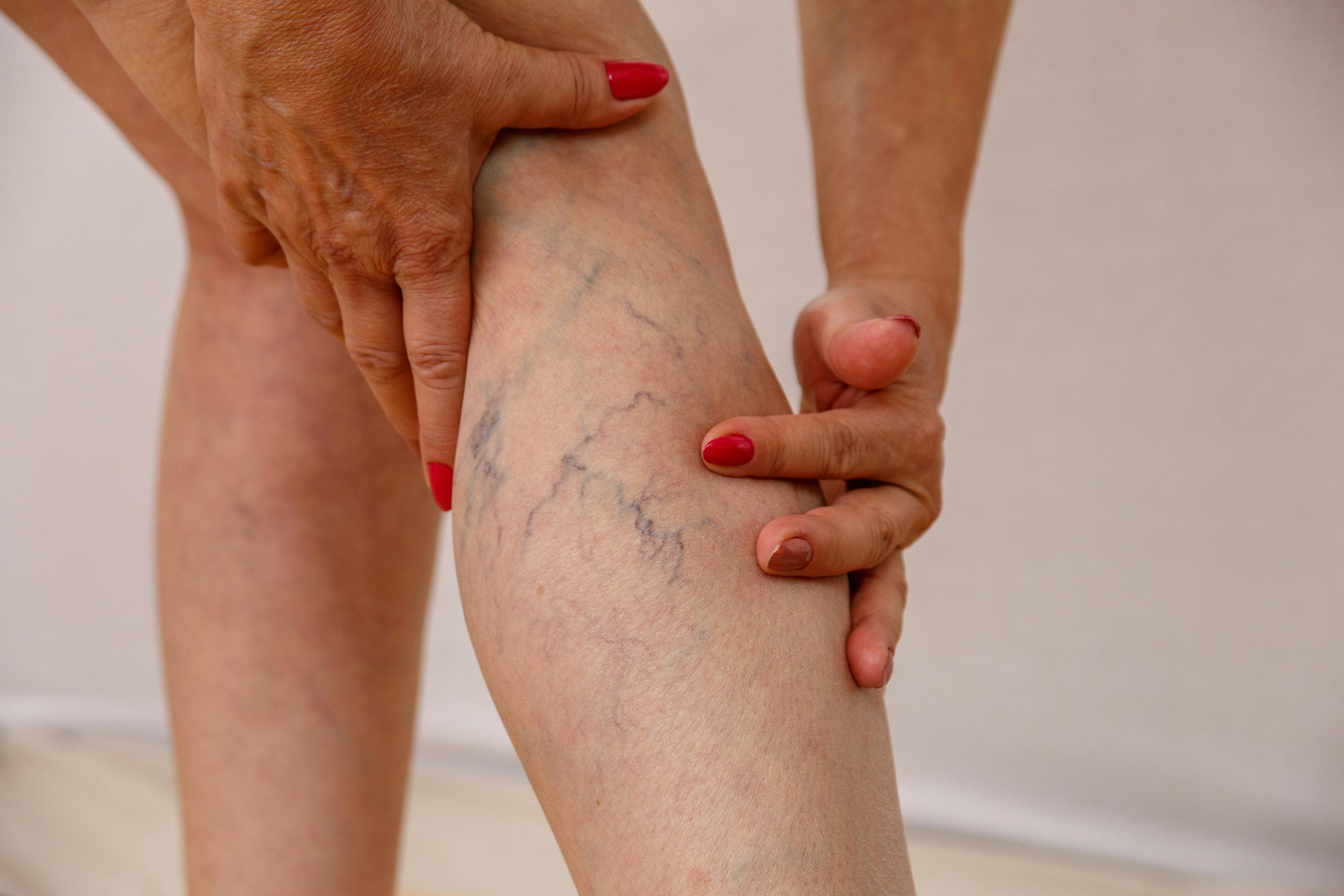
Varicose Veins
Bulging, twisted veins, often in the legs, caused by weak or damaged valves. Varicose veins can cause aching, swelling, skin changes, or discomfort. Treatments may include compression therapy, sclerotherapy (injecting a solution to close the vein), or minimally invasive procedures like endovenous ablation to close or remove damaged veins.
Disorders of Veins and Arteries
This category includes conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT)—a blood clot in a deep vein—and chronic venous insufficiency, where veins struggle to send blood back to the heart. It also covers arterial aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), and other vascular anomalies.
Treatment may involve blood thinners, clot removal procedures, stenting, or surgical repair. Preventing blood clots is also critical for high-risk patients and may necessitate compression therapy, medications, or movement strategies to reduce risk during recovery, hospitalization, or travel.
Protecting Your Vascular Health
Managing vascular disease goes beyond procedures. Your care plan may include smoking cessation, cholesterol management, blood pressure control, diabetes care, exercise therapy, and routine vascular screenings. Our vascular specialists focus on early detection, minimally invasive treatments, and long-term prevention to reduce the risk of stroke, limb loss, or serious complications.