Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most common causes of female infertility, affecting an estimated 6% to 12% of women of reproductive age in the U.S. This hormonal condition can disrupt menstrual cycles, impact fertility, and lead to other long-term health issues.
Learning about your treatment options allows you to take informed steps toward managing symptoms and preventing long-term complications. Treatment typically focuses on correcting hormonal imbalances, supporting reproductive health, and addressing metabolic concerns through individualized care.
What is PCOS?
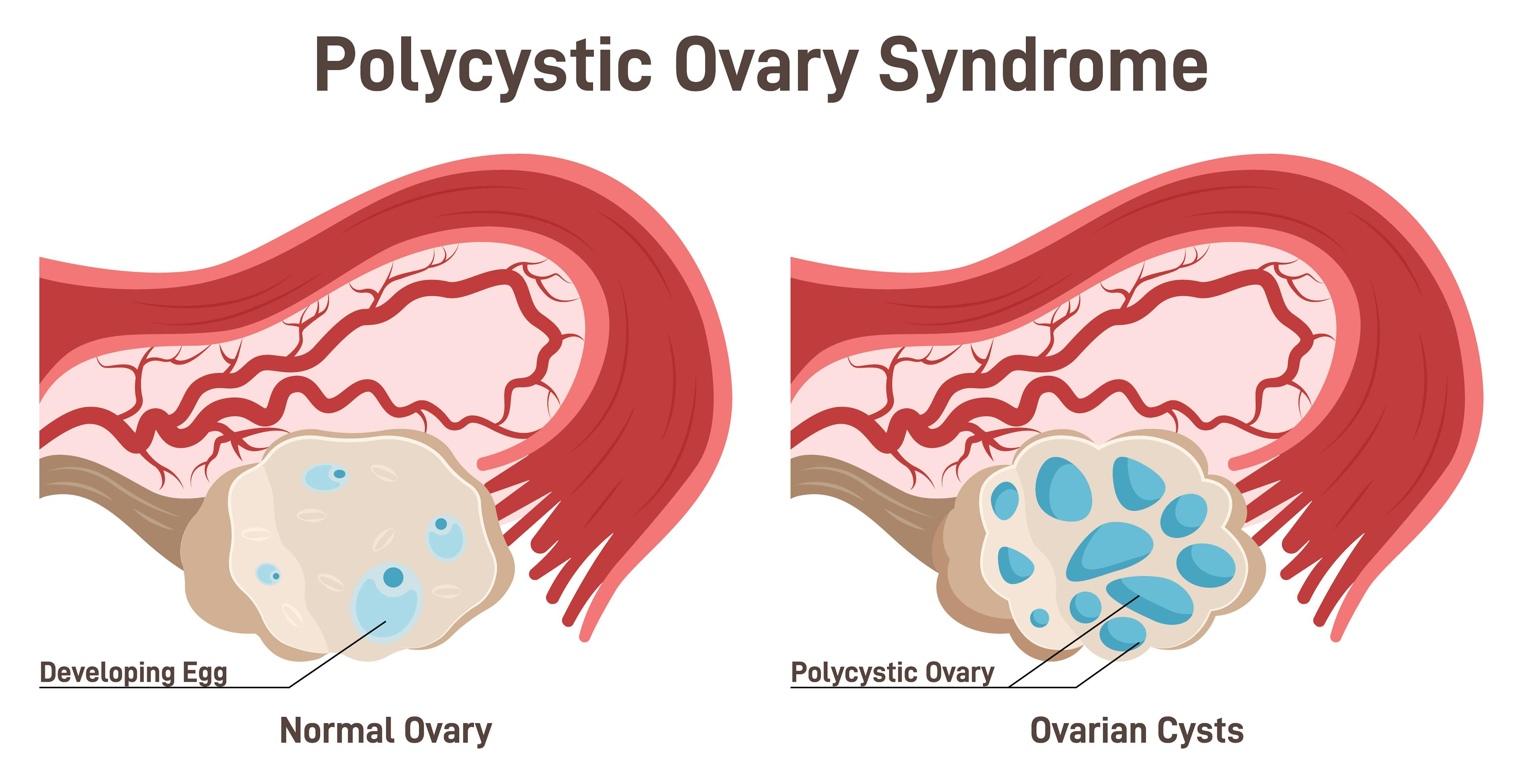
PCOS results from imbalances within the endocrine system, disrupting ovarian function and hormone levels. Women with PCOS typically experience irregular menstrual periods, elevated androgen levels, and the presence of multiple small follicles in the ovaries, often referred to as cysts. While the precise cause is unknown, contributing factors usually include insulin resistance, genetic predisposition, inflammation, and environmental influences.
PCOS Symptoms
Symptoms of PCOS can vary widely in type and severity. Below are some of the most commonly reported signs linked to the condition.
Irregular Periods & Ovulation Issues
Women with PCOS frequently experience menstrual irregularities due to inconsistent ovulation. Periods may occur less frequently or last longer than usual, making menstrual cycles unpredictable. This irregularity often complicates fertility planning, potentially leading to difficulties becoming pregnant.
Hormonal Imbalances & Androgen Levels
PCOS often involves higher-than-normal levels of androgens, hormones typically associated with male characteristics. The resulting hormonal imbalance can cause symptoms such as increased hair growth (hirsutism), acne, and hair loss or thinning. If you suspect your symptoms may be related to a hormone imbalance, it may be helpful to consult with an OB/GYN or endocrinologist for further evaluation and specialized care.
Weight Gain & Insulin Resistance
Many individuals with PCOS experience insulin resistance, leading to weight gain, especially around the abdomen. Insulin resistance affects about 70% of women with PCOS and increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Acne, Hair Growth, & Hair Loss
Due to elevated androgen levels, individuals with PCOS may develop persistent acne, unwanted hair growth on the face and body, or experience significant hair loss or thinning of scalp hair, which may impact self-esteem and body image.
How is PCOS Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of PCOS involves a comprehensive evaluation of symptoms, blood tests, and imaging studies. Early diagnosis can help reduce the risk of long-term complications and lead to quicker relief from disruptive symptoms.
Blood Tests
Hormone testing is essential for the diagnosis of PCOS. Blood tests measure androgen levels, luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These tests also assess insulin resistance and help identify related conditions such as diabetes, high cholesterol, and other metabolic concerns.
Ultrasound to Detect Ovarian Cysts
A pelvic ultrasound is often used to visualize the ovaries and detect cysts or enlarged follicles. This painless imaging procedure provides clear information to help your OB/GYN evaluate for PCOS.
Evaluating Symptoms & Medical History
Your healthcare provider will review your symptoms, menstrual cycle patterns, and family medical history. This thorough evaluation helps identify signs of PCOS and rule out other potential conditions.
PCOS Services at CLS Health
PCOS Management
PCOS management involves a multidisciplinary approach. Treatments often combine lifestyle adjustments, medication, and regular monitoring to control symptoms and reduce the risk of related health issues such as diabetes and heart disease.
Weight Loss & Nutritional Counseling
Weight management plays an important role in controlling PCOS symptoms and lowering related health risks. Nutritional counseling, focusing on balanced meals, low-glycemic foods, and regular physical activity, can help improve insulin sensitivity and support sustainable weight loss.
Hormonal Therapy
Hormonal treatments, such as birth control pills, help regulate menstrual cycles and lower androgen levels. Medications like spironolactone may also be prescribed to address symptoms related to excess androgens, such as acne or unwanted hair growth.
Natural OTC Supplements
For many patients, especially those not comfortable with hormonal treatments, natural over-the-counter (OTC) supplements offer a gentler path to symptom relief. These supplements may help restore hormonal balance, ease metabolic issues like insulin resistance, and address concerns such as acne, weight fluctuations, or cycle irregularity. While not a cure, they can be effective components of a broader treatment strategy, especially for patients who prefer not to use birth control or prescription medications.
Fertility Support & Reproductive Care
PCOS frequently causes fertility issues due to irregular ovulation. We offer fertility treatments, including medications such as Clomiphene and Letrozole to stimulate ovulation and improve pregnancy rates. If medication alone is ineffective, assisted reproductive techniques such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be considered.
Annual Check-ups
Regular women’s health exams and annual check-ups are essential for ongoing PCOS management. These visits provide opportunities for routine screenings, symptom monitoring, and preventive care to maintain reproductive health.
FAQs
Currently, there is no cure for PCOS, but symptoms can often be managed through lifestyle adjustments and medical treatments. Treatment may help regulate menstrual cycles, lower androgen levels, and target concerns such as acne, excessive hair growth, or difficulty with fertility, depending on your symptoms.
The recommended diet for PCOS emphasizes consuming low-glycemic index foods, lean proteins, healthy fats, whole grains, and ample vegetables. Research demonstrates that this dietary approach significantly reduces insulin resistance, assists weight loss, and improves overall metabolic health.
Yes, PCOS is one of the leading causes of infertility due to irregular ovulation, affecting approximately 70% to 80% of women diagnosed. With medical assistance, however, many women successfully conceive and maintain healthy pregnancies.
Women with PCOS are at a significantly increased risk for developing type 2 diabetes, primarily due to insulin resistance. Studies show that approximately 50% of women with PCOS will develop diabetes or prediabetes by age 40 without intervention.
If you experience irregular menstrual cycles, excessive facial or body hair growth, persistent acne, unexplained weight gain, and scalp hair thinning, you may have PCOS. To determine the cause of your symptoms, consult a healthcare provider who can perform a clinical evaluation, blood tests, and ultrasound imaging.
