To this day, strokes remain one of the leading causes of disability and death worldwide, often striking suddenly and without warning signs. Hemorrhagic strokes, which involve bleeding in the brain, are less common than ischemic strokes but often more severe. They require immediate attention and specialized treatment. However, with the right medical care, rehabilitation, and lifestyle support, many people recover important functions and continue living meaningful, fulfilling lives.
Note: If you or someone you know is experiencing stroke symptoms, please call 911 immediately. Every minute counts when treating a stroke.
What Is a Hemorrhagic Stroke?
A hemorrhagic stroke happens when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures, causing bleeding into or around brain tissue. This bleeding increases pressure on the brain and disrupts vital functions. As opposed to an ischemic stroke, which occurs when a blood clot blocks blood flow to the brain, a hemorrhagic stroke is caused by a vessel breaking open. Understanding the difference between ischemic vs. hemorrhagic stroke is important because treatment approaches are very different.
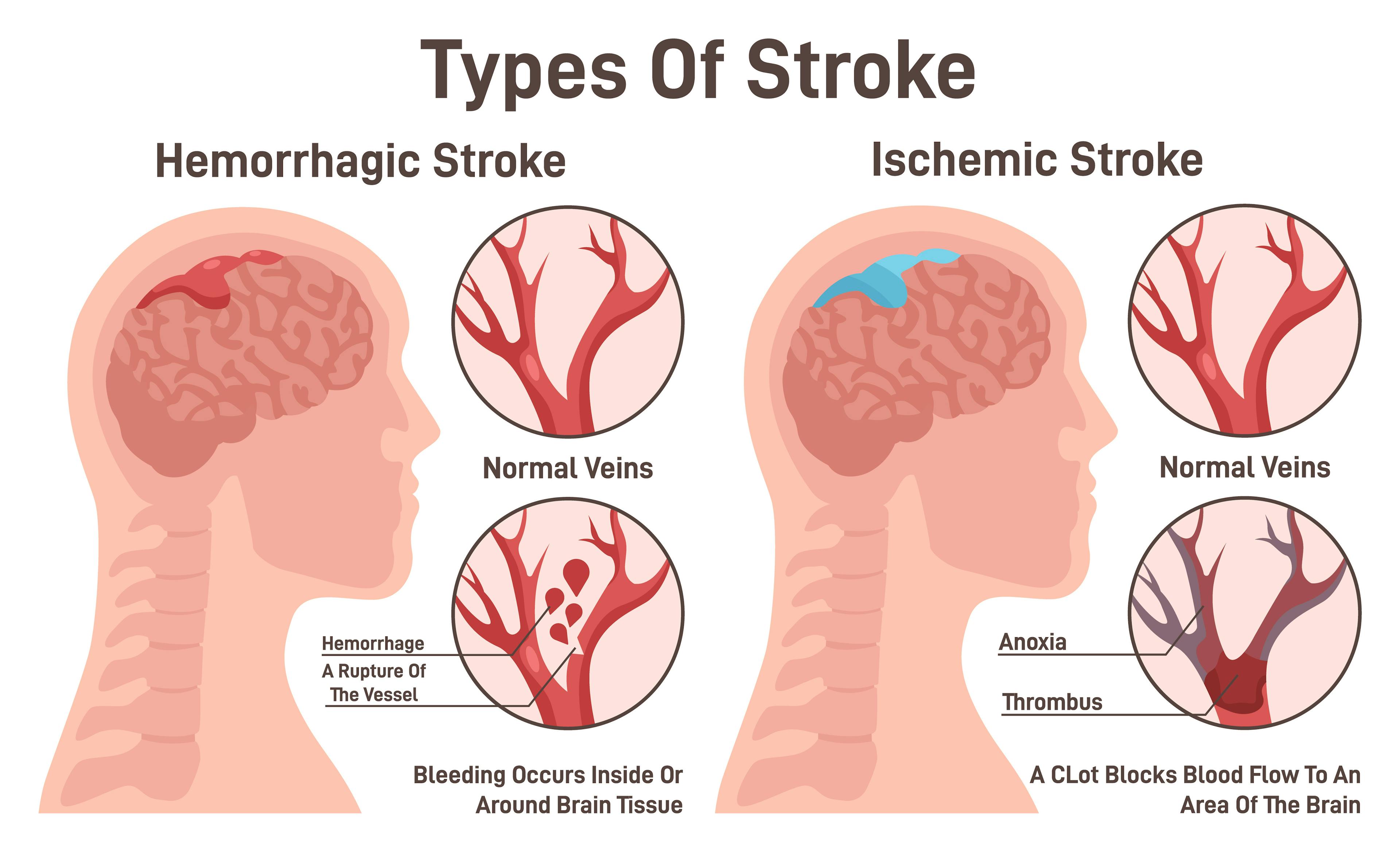
Hemorrhagic Stroke vs. Ischemic Stroke
While both types of stroke can cause sudden neurological symptoms, their causes are distinct.
- Hemorrhagic stroke: bleeding in or around the brain due to a ruptured blood vessel.
- Ischemic stroke: blockage of a vessel that prevents blood and oxygen from reaching brain tissue.
Symptoms may overlap, including weakness, slurred speech, or vision changes, but the urgency of accurate diagnosis cannot be overstated. For strokes, imaging tests such as CT scans are critical in showing whether the cause is ischemic or hemorrhagic, allowing doctors to deliver life-saving treatment.
Causes of Hemorrhagic Stroke
Several factors can increase the risk of a hemorrhagic stroke. The most common cause is high blood pressure (hypertension), which weakens artery walls over time. Other causes include:
- Aneurysms: bulging weak spots in arteries that can rupture.
- Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs): abnormal tangles of blood vessels in the brain.
- Head trauma: injuries that damage blood vessels.
- Other risk factors: blood-thinning medications, liver disease, and certain genetic conditions.
Hemorrhagic Stroke Risk Factors
In addition to direct causes, certain factors make a person more likely to experience a hemorrhagic stroke:
- Family history of stroke or aneurysm
- Prolonged uncontrolled high blood pressure
- Smoking or heavy alcohol use
- Older age, particularly after 55
- Chronic health conditions such as diabetes or heart disease
Symptoms of Hemorrhagic Stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke symptoms usually appear abruptly and progress quickly. Common symptoms include:
- A sudden, severe headache (often described as “the worst headache of my life”)
- Weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg, usually on one side
- Vision problems or slurred speech
- Loss of balance or coordination
- Nausea, vomiting, confusion, or loss of consciousness
Hemorrhagic Stroke Treatment
Stroke treatment begins with emergency care and stabilization. Patients are often admitted to intensive care to manage bleeding, pressure in the brain, and vital functions. Options include:
- Medications to control blood pressure and support blood clotting.
- Surgical procedures such as clipping or coiling an aneurysm, removing blood clots, or draining excess fluid.
- Rehabilitation, which may involve physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy, is used to restore lost function.
The approach depends on the cause, location, and severity of bleeding, but it’s always best to check in with your PCP or neurologist to help guide your treatment process.
Recovery & Quality of Life After Hemorrhagic Stroke
Recovery varies widely but often requires weeks or months of rehabilitation. Patients may need:
- Physical therapy to regain strength and coordination.
- Occupational therapy to relearn daily activities.
- Speech therapy for communication challenges.
Long-term effects may include difficulties with mobility, memory, or emotions. Many stroke survivors go on to achieve meaningful recovery with the right support. Addressing mental health through counseling, community resources, caregiver involvement, and structured rehabilitation can boost confidence and overall well-being.
Positive lifestyle changes—like managing blood pressure, enjoying a balanced heart-healthy diet, staying active with safe exercise, and avoiding smoking—can further strengthen health and lower the risk of another stroke, helping survivors live fuller, healthier lives.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
The acronym BEFAST helps identify the warning signs of stroke:
- Balance: sudden loss of balance or coordination
- Eyes: vision changes or loss in one or both eyes
- Face: drooping on one side of the face
- Arm: weakness or numbness in one arm
- Speech: slurred or hard-to-understand speech
- Time: call 911 immediately
Seconds save brain cells — if you suspect a stroke, don’t wait, as it could potentially be life-threatening if treatment is delayed.
Find Personalized Stroke Care Services in Houston at CLS Health
Hemorrhagic strokes are medical emergencies that require fast diagnosis and treatment. Because of this, being aware of the symptoms and acting quickly can save lives and improve recovery. With early recognition and treatment, many patients regain independence and improve their quality of life. If you or a loved one is living with the effects of a stroke, post-stroke rehabilitation support is available. Find a provider for stroke evaluation and rehabilitation.
Book an appointment today for stroke care services in the Houston area.

